Stereo system speakers are essential for anyone who appreciates high-quality audio. Whether you’re a casual listener, a home theater enthusiast, or an audiophile, understanding stereo speakers will help you make informed decisions to enhance your listening experience. This guide covers everything you need to know about home audio systems, including types, key features, setup, and tips for choosing the right ones for your needs.
What Are Stereo System Speakers?
Stereo speakers are designed to produce sound from two distinct channels — left and right. Unlike mono speakers that use a single channel, stereo systems create a wider, more immersive soundstage. This stereo effect allows listeners to experience audio as if it’s coming from multiple directions, adding depth and realism to music, movies, and games.
A standard stereo setup includes two speakers (referred to as the left and right speakers). These speakers work together to create spatial audio, making instruments and sounds appear to come from different locations, mirroring how we perceive sound in real life.
Types of Stereo System Speakers
1. Bookshelf Speakers
Bookshelf speakers are compact and designed to sit on shelves, desks, or stands. They’re ideal for small to medium-sized rooms and provide excellent sound quality for their size. While they lack the bass response of larger models, they are a popular choice for casual listening and smaller audio setups.
Pros: Compact, affordable, versatile.
Cons: Limited low-frequency response.
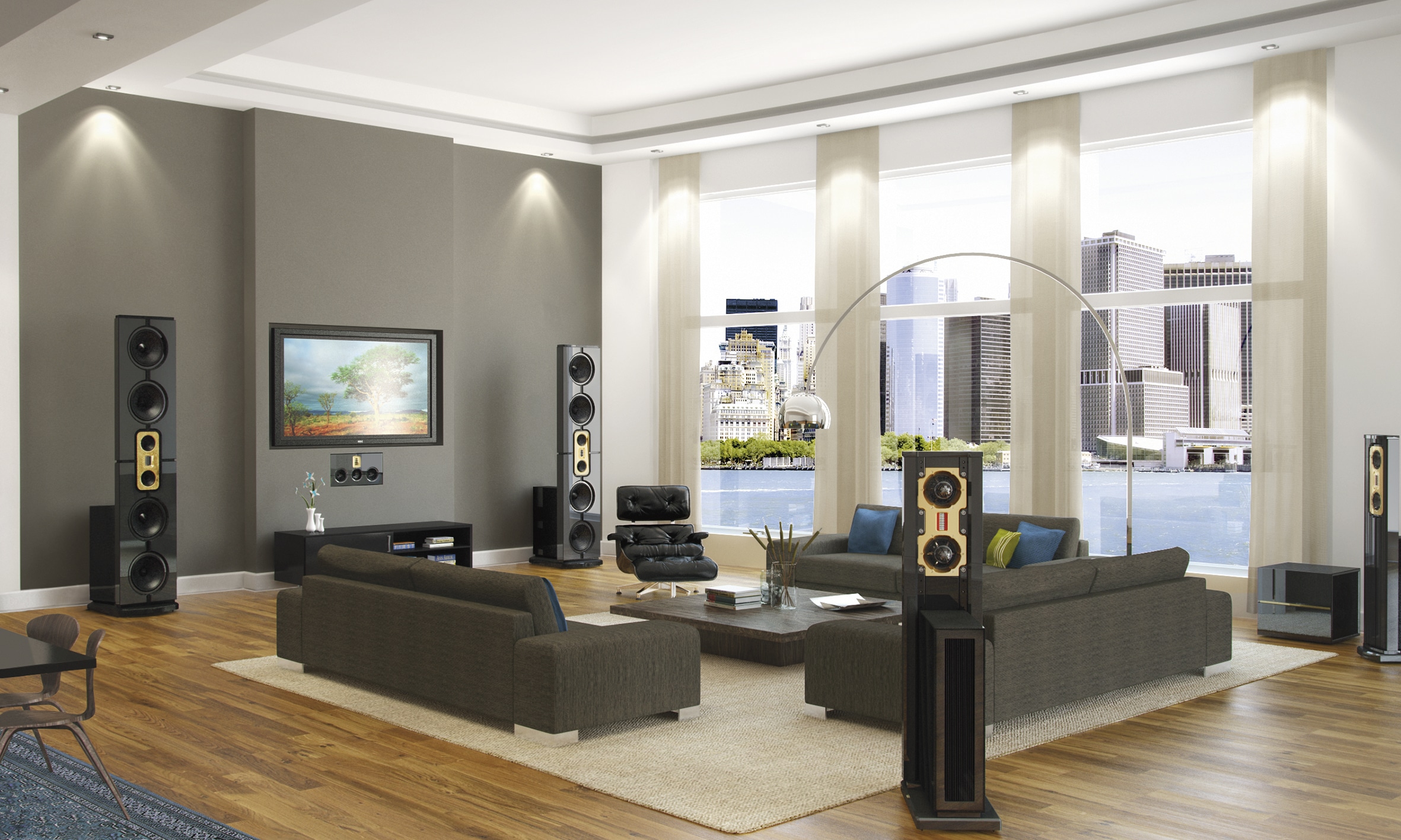
2. Floor-Standing Speakers
Also known as tower speakers, these are larger, free-standing speakers that deliver powerful and full-range sound. Their larger cabinets allow for multiple drivers (woofers, tweeters, and sometimes midrange speakers), making them capable of producing deeper bass and higher volumes.
Pros: Excellent sound quality, full-range audio, great for large rooms.
Cons: Larger footprint, typically more expensive.
3. In-Wall and In-Ceiling Speakers
For a sleek and unobtrusive look, in-wall and in-ceiling speakers are installed directly into walls or ceilings. These are ideal for home theaters or whole-house audio systems, providing clean aesthetics without sacrificing sound quality.
Pros: Space-saving, visually appealing.
Cons: Complex installation, harder to upgrade or move.
4. Powered (Active) Speakers
Powered speakers have built-in amplifiers, meaning they don’t require an external amplifier or receiver. These are great for desktop audio setups, Bluetooth connections, or minimalist systems.
Pros: Easy setup, no need for an external amp.
Cons: Can be less customizable.
5. Passive Speakers
Passive speakers require an external amplifier or AV receiver to power them. Most traditional stereo systems use passive speakers, which offer greater flexibility in terms of upgrading components.
Pros: Highly customizable, often better sound quality.
Cons: Requires additional components (amplifier/receiver).
Key Components of Stereo Speakers
1. Drivers
Drivers are the heart of a speaker, responsible for producing sound. The most common types include:
- Tweeters — Handle high-frequency sounds (treble).
- Woofers — Handle low-frequency sounds (bass).
- Midrange Drivers — Handle frequencies between the tweeter and woofer.
2. Crossovers
Crossovers are internal circuits that direct specific frequencies to the appropriate drivers. For instance, high frequencies are sent to the tweeter, while low frequencies are sent to the woofer. A good crossover ensures balanced and clear sound.
3. Cabinet Design
The speaker cabinet houses the drivers and crossover. Cabinet design affects sound quality, with materials and construction influencing resonance and overall acoustics. Common cabinet types include sealed (acoustic suspension) and ported (bass reflex) designs.